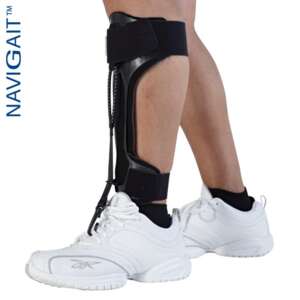
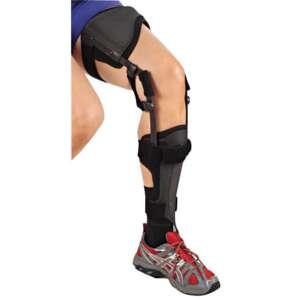
BlueROCKER® 2½
The Foot Drop Orthosis BlueROCKER® 2 ½ has the same dynamic functions and stability as a BlueROCKER® 2.0 with the exception that the 2 ½ has a lower heel height, 7 mm, to adapt to modern shoes. The toe lift is also slightly lower, which results in more space in the toe box. Since the start in 1997 the Allard AFO has been the market leader with its unique functions and dynamic properties.
BlueROCKER® 2 ½ has all MikroFIX pre-applied to simply fitment of the padding. The strap solution is the same as on 2.0, made from a durable and strong material. The straps can be applied for either inside or outside closure on the orthosis. The foot plate on BlueROCKER® 2 ½ gives more space in the toe box. It is always important to adapt any Allard AFO to the heel height of the shoe. Read more about this in the Allard AFO Professional Instructions.
Recommended Range Of Application
BlueROCKER® is designed to manage footdrop in conditions such as Stroke, Multiple Sclerosis, Post Polio Syndrome, Muscular Dystrophy, Spinal Cord Injuries, Traumatic Brain Injuries, Guillian-Barre Syndrome, Charcot-Marie-Tooth, Myelomeningocele, Neuropathy or Cerebral Palsy. BlueROCKER® 2.0 is designed to support gait in conditions such as Posterior Tibialis Tendon Dysfunction (PTTD) and toe amputations. BlueROCKER® can also be used for partial foot amputations, most proximal level is Chopart.
Contraindications
BlueROCKER® 2 ½ should not be used when patients present with foot and/or leg ulcers, moderate to severe edema, moderate to severe foot deformities, severe proximal deficits (e.g. quadriceps spasticity, genu valgum or varum, genu recurvatum), severe spasticity.
Other
More about fitting and product selection can be found in the Allard AFO Professional Instruction.
-
User Instruction Allard AFO (883.54 KB)
-
Professional Instruction AllardAFO (2.16 MB)
-
Partial Foot Brochure (1.59 MB)
-
Carbon Composite AFO Technology Brochure (1.91 MB)
-
AllardAFO - a sustainable choice (2.04 MB)
-
Brochure AllardAFO (1.13 MB)
-
Return form AllardAFO (121.71 KB)
-
Warranty Information AllardAFO (47.34 KB)
-
Medical Reference Paper (1.89 MB)
Author: Danielsson A, Stibrant Sunnerhagen K.
Source: J Rehabil Med 2004; 36: 165–168
Author: ANI MNATSAKANIAN BS et al.
Source: Muscle Nerve 000:000–000, 2016
Author: Altschuck N. et al
Author: Roberts Joffe, Fredrik Forsberg, Henrik Lycksam, Anders Sjögren
Source: ICTMS 2017 - 3rd International Conference on Tomography of Materials and Structures, 26-30 June 2017, Lund, Sweden
Author: Shuman BR, Espesito ER
Source: Journal of Biomechanical Engineering. JANUARY 2022, Vol. 144 / 011004-1
Author: Shuman et al.
Source: Journal of NeuroEngineering and Rehabilitation (2023) 20:11
Author: Megan M. Grunst, Robert C. Wiederien and Jason M.
Source: A systematic review Prosthetics and Orthotics International 2023
Author: Burke K1,2, Cornell K1,3, Swartz Ellrodt A1,2, Grant N1,2, Paganoni S2,4,5 and Sadjadi R1,2*
Source: CMT study.2021
Preliminary research suggests the use of a kinetic return ankle foot orthosis is associated with small but significant shortterm increases in calf circumference, which in turn suggests this type of device might reduce or protect against the risk of disuse muscle atrophy.
Author: Robert H. Meier, CO, BOCO; David C. Ruthsatz, CO, CPA; and Daniel, Cipriani, PT, PhD.
Source: Lermagazine 2014